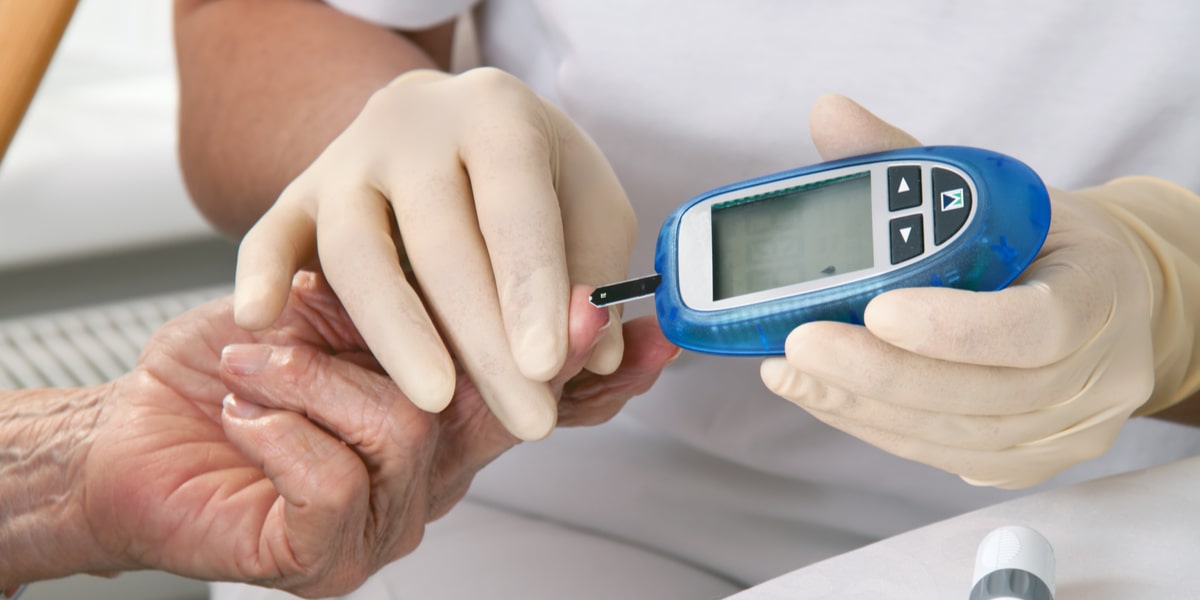
Blood glucose meters are essential tools for individuals living with diabetes, enabling them to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and make informed decisions about managing their condition. These portable devices provide quick and accurate measurements of blood glucose levels, allowing individuals to track fluctuations throughout the day and adjust their diet, medication, and lifestyle accordingly. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the functionality, features, usage, and advancements of blood glucose meters, highlighting their importance in diabetes management and the role they play in promoting health and well-being.
Understanding Blood Glucose Meters:
Blood glucose meters, also known as glucometers or blood sugar meters, are handheld devices used to measure the concentration of glucose in a small sample of blood. Most blood glucose meters utilize a technique called amperometric glucose oxidase-based biosensor technology to measure blood glucose levels. This technology involves the oxidation of glucose by glucose oxidase, producing a measurable electrical current that is proportional to the glucose concentration in the blood sample.
Key Features of Blood Glucose Meters:
Modern blood glucose meters offer a range of features and capabilities to meet the diverse needs of individuals with diabetes. Key features of blood glucose meters include:
- Accurate Measurements: Blood glucose meters provide accurate and reliable measurements of blood glucose levels, allowing individuals to monitor their condition with confidence and precision.
- Small Sample Size: Blood glucose meters require only a small drop of blood (typically 0.5 to 1 microliter) for testing, minimizing discomfort and inconvenience for users, especially those who need to test frequently.
- Rapid Results: Most blood glucose meters deliver results within seconds, allowing individuals to obtain real-time information about their blood sugar levels and take immediate action if necessary.
- Memory Storage: Many blood glucose meters are equipped with memory storage capabilities, allowing users to store and review previous test results over time. This feature enables individuals to track trends, identify patterns, and make informed decisions about their diabetes management.
- Data Connectivity: Some blood glucose meters offer connectivity features, such as Bluetooth or USB connectivity, allowing users to transfer test results to a computer, smartphone, or cloud-based diabetes management platform for further analysis and sharing with healthcare providers.
- User-Friendly Design: Blood glucose meters are designed with user convenience and ease of use in mind, featuring intuitive interfaces, large display screens, and ergonomic designs for comfortable handling and operation.
Usage and Testing Procedure:
Using a blood glucose meter involves the following steps:
- Prepare the Meter: Insert a test strip into the meter and turn it on. Ensure that the meter is calibrated and ready for testing.
- Prepare the Lancet Device: Use a lancet device to obtain a small drop of blood from a fingertip or alternate site, such as the palm or forearm. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper lancet placement and puncture depth.
- Obtain Blood Sample: Place the drop of blood on the designated area of the test strip. The meter will automatically draw the blood into the strip for testing.
- Wait for Results: The blood glucose meter will analyze the blood sample and display the results on the screen within seconds. Record the result in a logbook or on a digital diabetes management platform for future reference.
- Dispose of Waste: Safely dispose of the used lancet and test strip according to local regulations and guidelines for medical waste disposal.
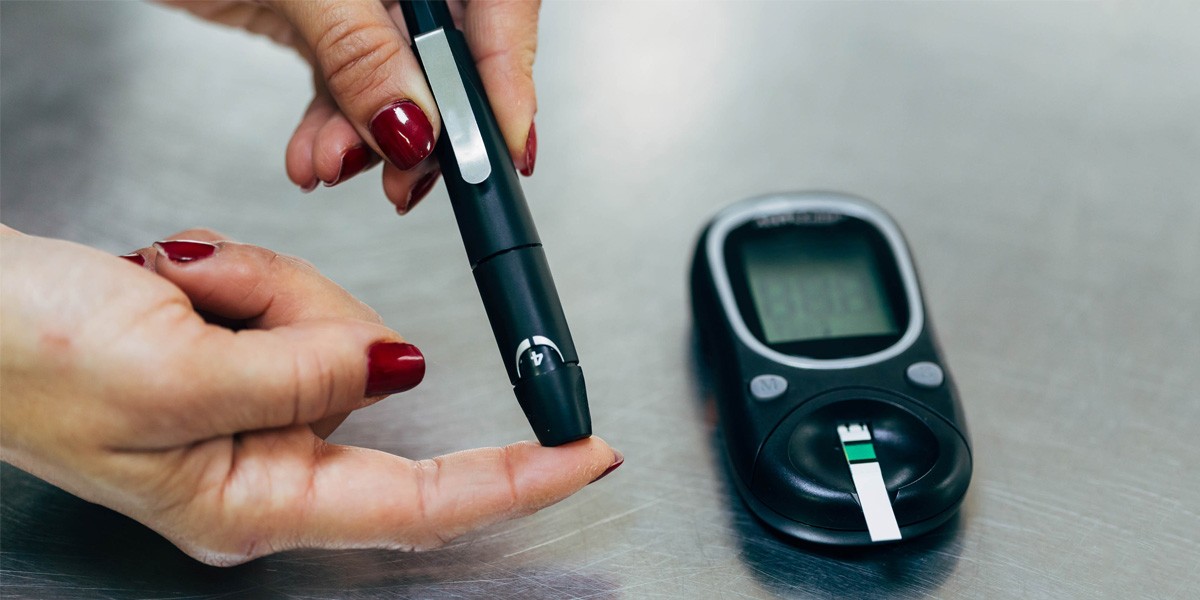

Advancements in Blood Glucose Monitoring:
Recent advancements in blood glucose monitoring technology have led to the development of innovative features and improvements in accuracy, convenience, and connectivity. Some notable advancements include:
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems: CGM systems use wearable sensors to continuously monitor interstitial glucose levels throughout the day and night, providing real-time data and alerts to users and healthcare providers. CGM systems offer insights into glucose trends, patterns, and fluctuations, enabling proactive diabetes management and reducing the need for frequent fingerstick testing.
- Integrated Insulin Pump Systems: Some blood glucose meters are integrated with insulin pump systems, allowing individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels and deliver insulin doses using a single device. These integrated systems offer streamlined diabetes management and enhanced convenience for users.
- Smartphone Integration: Many blood glucose meters now offer smartphone integration, allowing users to sync test results directly to a mobile app for easy access, analysis, and sharing with healthcare providers. Smartphone apps may also provide additional features, such as reminders, trend analysis, and educational resources to support diabetes management.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Algorithms: AI-powered algorithms are being developed to analyze blood glucose data and provide personalized insights and recommendations for diabetes management. These algorithms can identify patterns, predict future glucose levels, and suggest optimal treatment strategies based on individual data and preferences.
The Importance of Regular Monitoring:
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential for individuals with diabetes to maintain optimal glycemic control and prevent complications. By tracking blood sugar levels throughout the day, individuals can identify patterns, trends, and factors that affect their diabetes management, such as diet, exercise, medication, and stress. Monitoring allows for timely adjustments to treatment plans, such as insulin dosages or meal timing, to keep blood glucose levels within target ranges and minimize the risk of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) or hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Additionally, regular monitoring provides valuable information for healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of treatment strategies, make informed decisions about medication adjustments, and provide personalized recommendations for diabetes management.
Empowering Self-Management and Engagement:
Blood glucose meters empower individuals with diabetes to take an active role in their self-management and engage proactively in their healthcare. By providing immediate feedback on blood sugar levels, these devices enable individuals to make informed decisions about lifestyle choices, such as meal planning, physical activity, and stress management, to optimize their diabetes management. Furthermore, blood glucose meters promote a sense of empowerment and autonomy by allowing individuals to monitor their condition independently and take control of their health on a day-to-day basis. With the knowledge and insights gained from regular monitoring, individuals with diabetes can better understand their condition, identify areas for improvement, and collaborate effectively with healthcare providers to achieve their diabetes management goals.
Conclusion:
Blood glucose meter play a critical role in the daily management of diabetes, enabling individuals to monitor their blood sugar levels accurately and make informed decisions about their health. With their compact design, rapid results, and advanced features, blood glucose meters empower individuals with diabetes to take control of their condition and optimize their quality of life. As technology continues to evolve, blood glucose monitoring devices are expected to become even more sophisticated, offering enhanced accuracy, connectivity, and personalized insights to support effective diabetes management. By leveraging the latest advancements in blood glucose monitoring technology, individuals with diabetes can achieve better glycemic control, reduce the risk of complications, and live healthier, more active lives.